Children at Risk of "Fatty Liver"
VIDA Y ESTILO
24-07-2023
web
Publicado: 24-07-2023 19:50:48 PDT
Actualizado: 24-07-2023 19:51:00 PDT
Fatty liver disease has a significant prevalence among children, and for prevention, imaging studies are recommended.
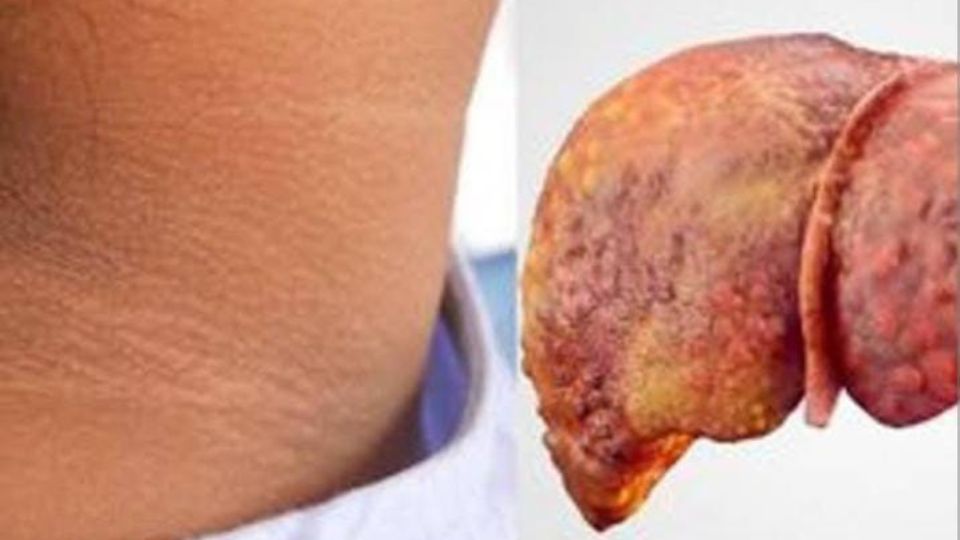
Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) is a condition characterized by the accumulation of fat in the liver, leading to inflammation of liver cells and varying degrees of fibrosis. Unlike alcohol-related liver diseases, NASH does not result from dangerous infections, but it can progress to significant fibrosis and cirrhosis.
Cirrhosis occurs when the liver sustains considerable damage, and the fibrous tissue gradually replaces liver cells, causing the liver to function inadequately. Some patients with cirrhosis may eventually require a liver transplant, a surgical procedure to remove the damaged liver and replace it with a new one.
Notably, NASH is quite common, affecting 20 percent of adults and 5 percent of children. Experts estimate that around 66 percent of adults and 20 percent of children in the United States are affected by this condition.
The main cause of this disease is obesity. Over the past decade, the obesity rate has doubled among adults and tripled among children and adolescents in the United States, which explains the increased prevalence of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis.
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease is considered a metabolic syndrome characterized by diabetes or prediabetes (insulin resistance), obesity, elevated blood lipids such as cholesterol and triglycerides, and hypertension.
According to the study, most adult patients do not exhibit visible symptoms, while children may experience abdominal pain in the middle or upper right area, fatigue, and sometimes areas of darkened skin (acanthosis nigricans), commonly found around the neck and armpits.
Diagnosis is confirmed through imaging studies, with liver ultrasound being the most common procedure, as it reveals the accumulation of fat in the liver.
Experts mention that there is currently no medical treatment to reverse fatty liver disease and eliminate fat from the liver. Therefore, they recommend weight loss for overweight or obese individuals, increased physical activity, maintaining a balanced diet, avoiding alcohol and unnecessary medications, taking medications to reduce lipids, insulin sensitizers (for diabetics), and, finally, reducing liver inflammation through the administration of antioxidant, anti-apoptotic, and anti-cytokine medications.

Cali - Baja
hace 8 horas
El evento se llevó a cabo en el edificio del Poder Ejecutivo ..

Cali - Baja
hace 9 horas
Ampudia defendió el primer lugar a lo largo del recorrid0 ..

Deportes
hace 9 horas
Antes de iniciar las carreras, las y los participantes realizaron un recorrido de reconocimiento y c ..
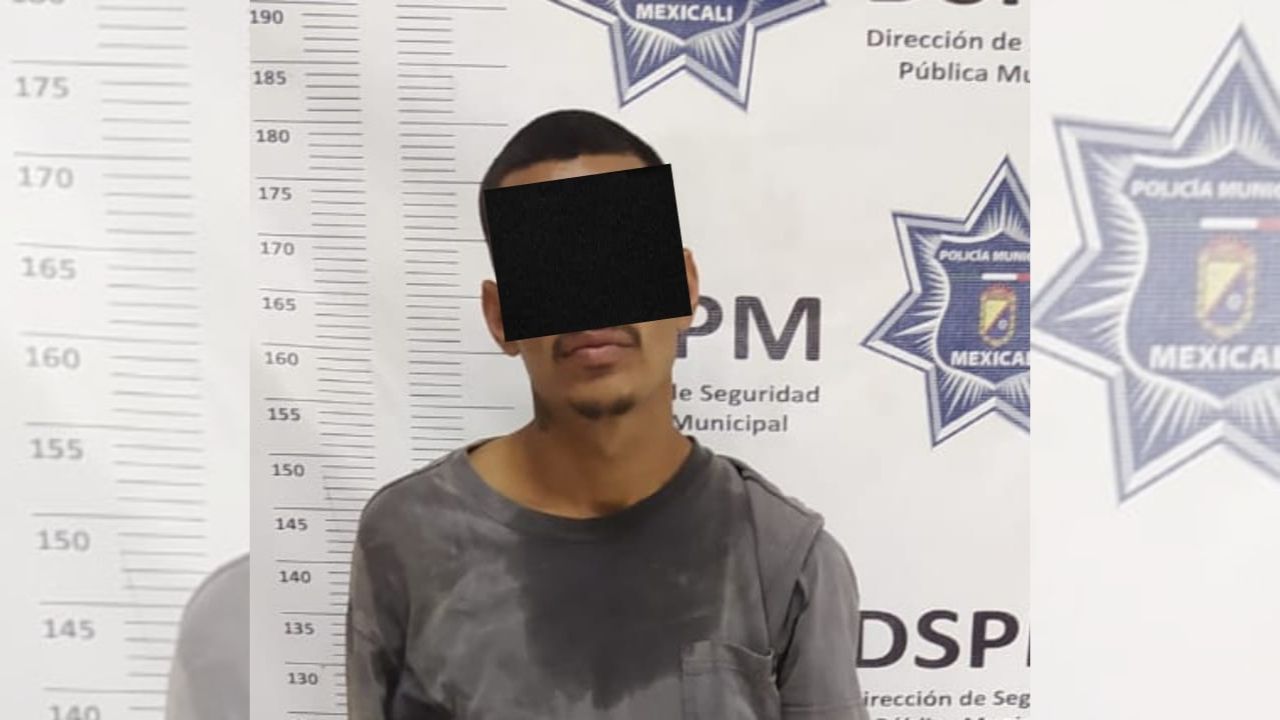

Policiaca
hace 9 horas
De acuerdo con la versión proporcionada por la parte quejosa, el sujeto que vestía con camisa gris, ..
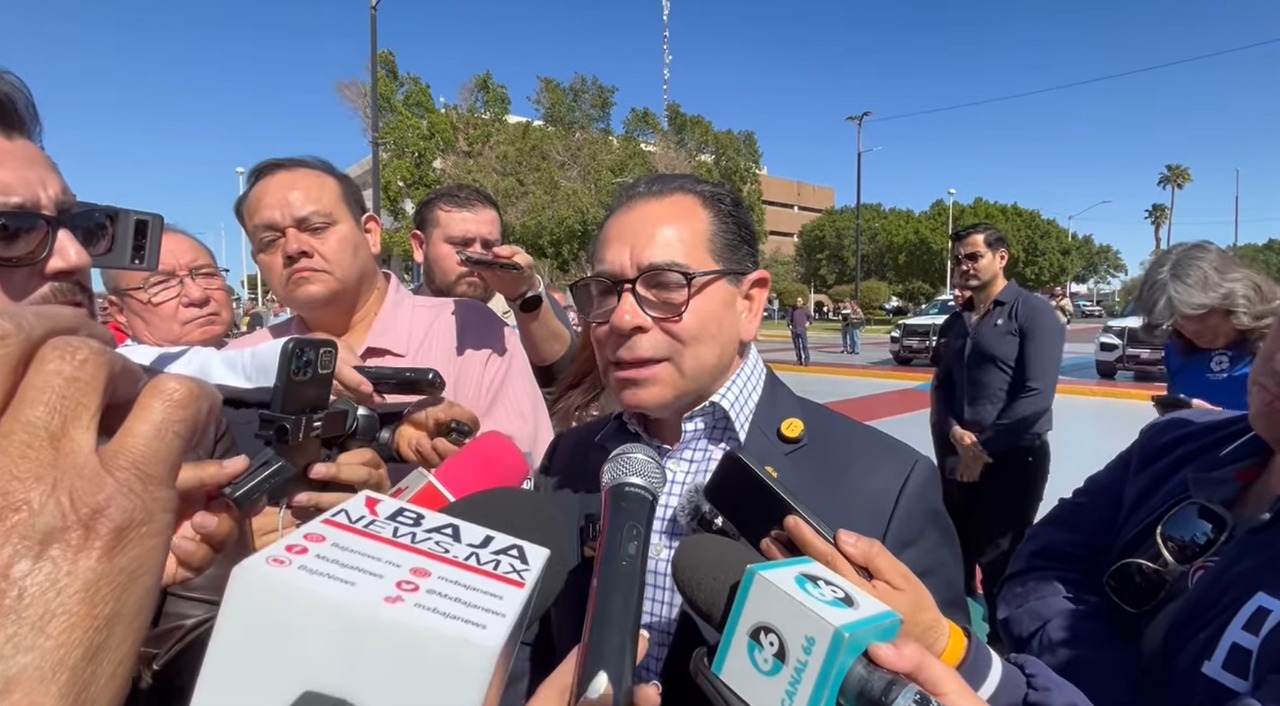

Cali - Baja
hace 9 horas
No se permitirá el consumo de bebidas alcohólicas en la vía pública ..
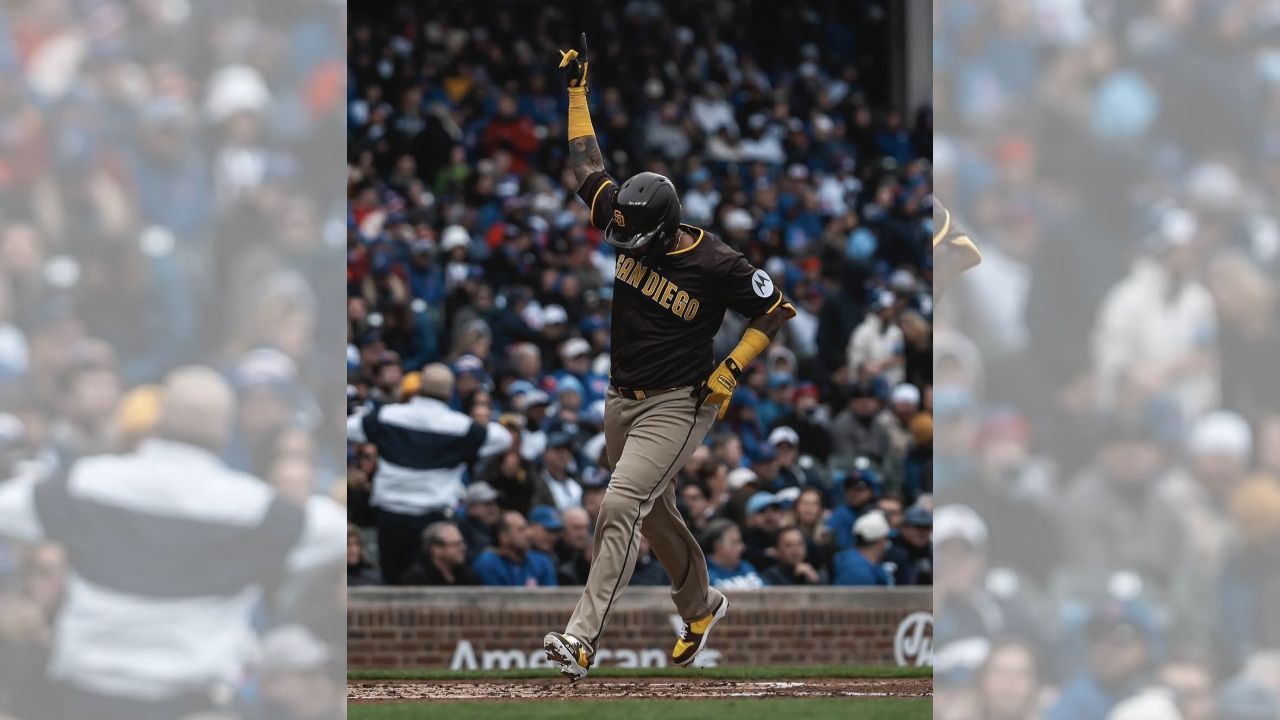

Deportes
hace 10 horas
El tercer juego de la serie entre San Diego y Chicago será este domingo ..

